Canada's new marijuana laws must attend to business: Don Pittis
Now is the time to make sure pot laws are in Canada's long-term interest
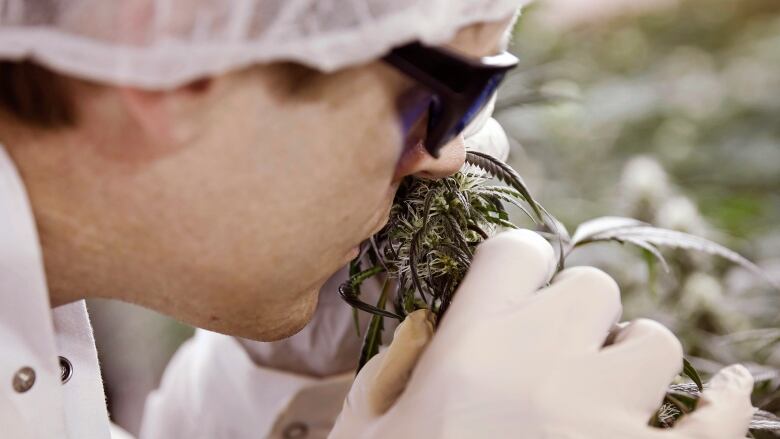

As ruralyouthhave known for more thana generation, growing pot, even in the Canadian climate,is not so difficult. A sunny patch between youngpines, a bit of fertilizer and seed and then go away till autumn.
The constrainton pot production has never been agricultural.
Marijuana laws have been in place for so long that there will be political pressure to make sure any changes put health and safety first as Canada leads the way on pot regulation.But as governments across the countryconsider how to liberalize the rules on thedistribution and use of cannabis, they are also laying the ground rules for a multibillion-dollar industry.
- World looking to Canada on pot legalization says health minister
- Canadian company's marijuana infused pods ready for brewing
There are two ways for Canadian governments to benefit from legal pot. Finance ministers may have been salivating over new tax revenue. But having a strong and functioning industry, andeven a major export sector, may providegreater opportunities for the economy.
The previous government's 2014licensing rules on medical marijuana opened the door to new entrants. Meanwhile, the Canadian Consortium for the Investigation of Cannabinoidsis a leader in medical marijuana research.
Explosive growth
But with a move to recreational use the business faces explosive growth, taking revenueout of the hands of illegal producers and importers and making all that income taxable.
In many ways it is a huge internationalopportunity, says David Sparling, an expert in agricultural systems and a professor at the Ivey School of Business.
"We are sitting in a place where we actually can be a leading supplier, if we act quickly," says Sparling, who studies agricultural supply management from crop to customer.
A strongsystem of regulation and quality control would make Canadian product credible on international markets. A clear legal framework for security and distribution wouldgive foreign investors a safe place to invest without worrying about the conflicts betweenfederal and state rules we have seen in the U.S.
But Sparlingsays the industry must be given the latitude to experiment, creatinggood product byimporting the best genetics from around the world. He says a successful recreational marijuana industry must not make the same early mistakes asCanadian vintnerswhoused local grapes to make bad wine.
"We don't want to spend a lot of time on that," says Sparling.
Cannabis appellationcontrle?
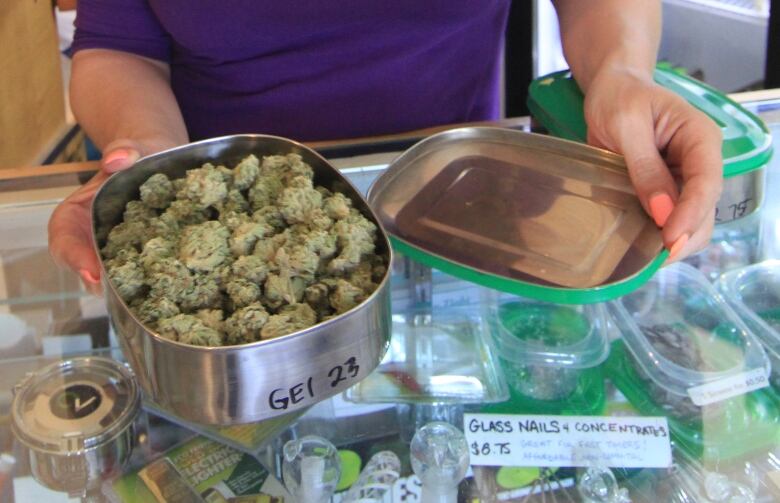

The current laws for medical marijuana are still very restrictive, says Barry Kurtzer, the president of DelShen Therapeutics, a company applying to start production near the mining town of Kirkland Lakein northeastern Ontario. He doesn't rule out expanding into production for the recreational market at some point in the future, andsays a widely distributed industry isgood for the Canadian economy in places like Kirkland Lake.
"Obviouslywith the downturn in the economy and the downturn in resources pricing, the area as a whole was significantly impacted," says Kurtzer, a medical doctor, who claims the company would provide about 100 local jobs after it is up and running.
The B.C. advantage
One of the places most ready for a truly open system of marijuana distribution and sale is British Columbia, where in 2003 the value of the industry was already said to beworth $6 billion. There, medical marijuana shopfronts havealready become a grey market business.
- Tilray, medical marijuana producer, brings in big bucks for Nanaimo
- Looking south for advice on legal pot
It is important to take advantage of the expertise of the people in the medical marijuana sector rather than turning distribution over to state bureaucracies, what some people call the liquor board model,saysUniversity of British Columbia professor Zach Walsh, who has studied the industry.
Walsh saysit would be a good business strategy to letbothsmall and large players have a hand in the game.
"Making sure that the full range of people are allowed to participate in this new economy is going to be important," says Walsh.
He says that just as with household production of beer and wine, the new rules should allow Canadians to grow some of their own pot. But finance ministers hungry for taxes shouldn't worry. As with home brewing, Walsh insists, pot growing will onlyattract hobbyists.
As to the danger of foreign giants taking over the industry as they have with the international beer sector, Walsh isn'tworried about that either. B.C. consumers have a culture and tradition of buying locally produced quality goods.
Besides, he says,"Maybe it'll be a big international business run by B.C."
Follow Don Pittis on Twitter@don_pittis
More analysisby Don Pittis











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)