After string of coyote attacks, B.C. officials urge people to stay out of Vancouver's Stanley Park
5-year-old boy attacked at 9:30 p.m. on Tuesday
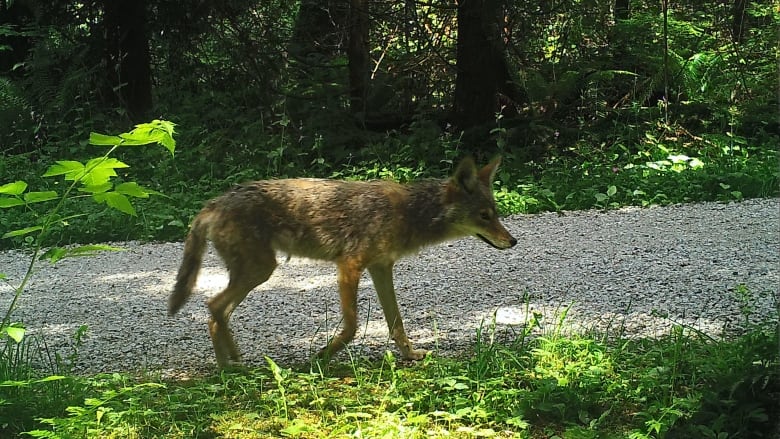

There has been another attack by a coyote in Vancouver's iconic Stanley Park, despite several of the animals being euthanized after dozens ofprevious incidents.
Scientists have struggled to find an explanation for the highly unusual behaviour, though experts say they are likely finding humanfood or even being fed.
The latest incident, which happened around 9:30 p.m. Tuesday, is the second recent coyote attackon a young child, according to B.C.'s Conservation Officer Service. A two-year-old boy was bitten on July 12, also at night.
"The boy was running ahead when a coyote lunged and bit him on the leg," the agency said of the mostrecent attack. "His parents chased the coyote away."
Authorities said the child received minor injuries and was later released from hospital.
The Conservation Officer Service declined an interview request Wednesday.
"It's of course really unfortunate," said Nadia Xenakis, urban wildlife programs co-ordinator with the Stanley Park Ecology Society. "To reiterate how strange this is, prior to this year, from 2001 to 2020 there were eight [coyote attacks] in the Lower Mainland. From December to now, we're nearing 40."
'We absolutely need signs'
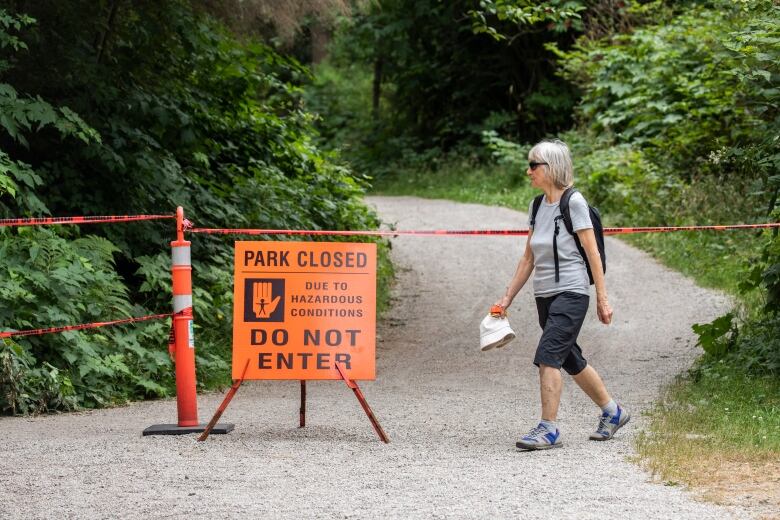
Xenakis said the group has created signage bearing the word "WARNING" in large lettersand a coyote's image to get the message across clearly and urgently to visitors and locals alike. But getting the city's approval for those signs took time.
"We absolutely need signs," Xenakis said. "I actually created the signage, but it took a while to get approval... with more graphic images for people who may not have English as their first language, so people who are from out of town can understand this is something they should be concerned about."
Park Rangers will be deploying more signage in the park to inform park users of the risk of encountering aggressive coyotes in the park, particularly early in the morning and after dark. We urge park users to stay off closed trails & never leave children unattended in the park.
—@ParkBoardA parks board spokesperson told CBC that "more aggressive" warning signs than the current ones are scheduled to be installed Thursday, so no out-of-town visitors will be left in the dark.
Despite human food being the most likely explanation for the unusual coyote behaviour, no animal-proof garbage cans have been installed yet, despite the society's recommendations.
Garbage can designs are still before the city's sanitation department and that will take some time.
Xenakis said without major changes in how people behave in the park, the estimated population of at least 12 coyotes there will likely continue to thrive thanks to human garbageand some who choose to ignore signs and feed the wild animalsanyway.
In mid-July, officers killed four of the animals in a bid to stop the attacks.
'It's highly unusual'
The conservation service again urged people"to stay out of Stanley Park" because of the "high risk of encountering an aggressive coyote."
"No one wants to see anyone injured by a coyote, especially a child."- B.C. Conservation Service
"We recognize and understand the public is concerned about these incidents," the service stated. "We are also concerned about the behaviour of coyotes in Stanley Park.
"No one wants to see anyone injured by a coyote, especially a child."
Scientists from the University of B.C. have been puzzling over what is causing the latest string of aggressive behaviour. They estimate the park has long been home to atleast 12 coyotes, so the new conflicts with people mostly in evening or night, and often targeting people who were running or jogging are not typical.
"It's highly unusual. This is behaviour we have not seen from coyotes around the world," saidKristen Walker, a wildlife biologist with UBC'sfaculty of land and food systems, in an earlier interviewwith CBCNews. "It is unprecedented."
A steady food source from park-goers, frequent late-night visitors, undisposed garbageand a loss of the animals' normal fear of humansare believed to be factors, they say.

With files from Chad Pawson












_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)