Will supervised injection sites work in Winnipeg? Addictions Foundation says they're not sure
Vancouver expert says benefits of safe injection sites include cost savings, fewer overdose deaths
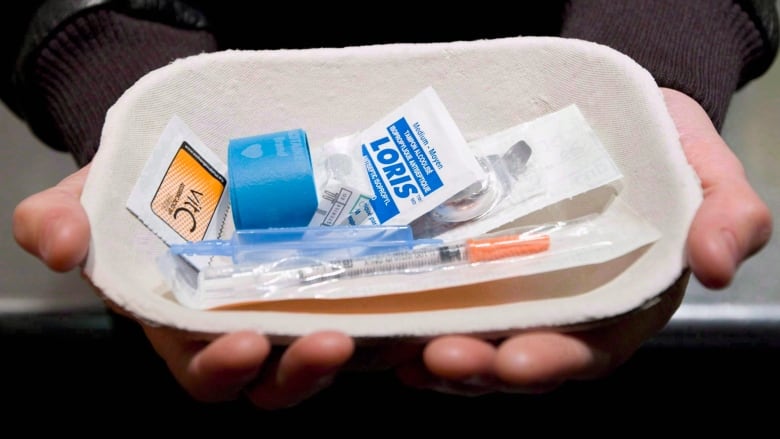
Despite calls from local community activists for supervised, or "safe"injection sitesto help prevent overdose deaths and keep needles off the streets, a local addictions expert says he believes theymay not work in Manitoba.
Ben Fry, CEO of the Addictions Foundation of Manitoba, said while sites in Vancouver have been effective, that is because theytargeted a concentrated population in a small area specifically, the Downtown Eastside.
In Winnipeg,the problem is more widespread than one neighbourhood, he said.
"The one thing that we believe from literature is that safe consumption sites do tend to be a model that's effective when there's a very narrow geographical area. What we see in Manitoba, that's not necessarily the case."

Manitoba, like all Canadian provinces, is dealing withthe availability of cheap crystal meth andopioidslikefentanyl. Overdose deaths from fentanylhave risen over the last number of years as the provincial health-care system strains to help addicts who have little access to resources.
"We have not seen evidence that it would be the most effective use of available funding to help those struggling with addiction in Manitoba," said a spokesperson for Health Minister Kelvin Goertzen.
"Manitoba, like other provinces, is still finalizing the terms of our bilateral agreement with the federal government, but we are currently working with stakeholders and department officials to develop proposals for the allocated federal funding. Those proposals must also consider the various forms of addiction in Manitoba, including addiction to alcohol."
The province is still anticipating reduced health funding from the federal government, said the spokesperson, which may impact addiction and mental health care.
Sites save lives, money: doc
If the province is struggling with health-care funding, then supervised injection sites should be apriority simply for the money and the lives they save, said Dr. M.J.Milloy.
Milloywas one of the principal investigators forInsite, Vancouver's largest supervised injection site and the first to open in Canada. He was mandated to do a scientific evaluationinto the benefits ofthe Insite model a freestanding, permanentsite in the Downtown Eastside with multiple booths for drug users and which is dedicated specifically to supervised injection.
Insite does not administer drugs but provides users a safe place to inject them, and makes medical personnel available to provide addictions treatment and other help.
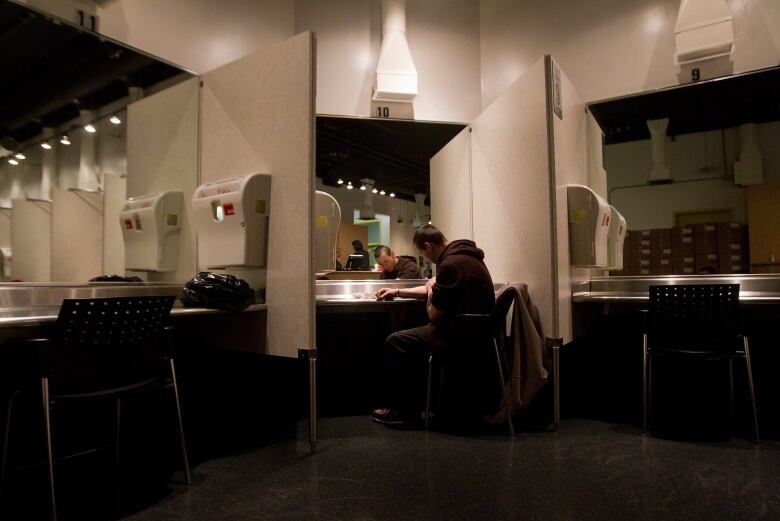

Thefive-year evaluation produced a body of scientific evidence that showed Insiteresulted in cost savings for the province of at least $14 million over 10 years. The study called those savings "conservative."
A second study looked at results in three specific areas, including overdose deaths, HIV and hepatits C infection rates, and methadone maintenance treatment.
There, researchers found a net savings of $18 million.
What we've learned over the past 10 yearsis there's a variety of different ways to implement supervised consumption services in ways that make sense for the local community.- Dr. M.J.Milloy
A third study also came to a similarconclusion, said Milloy.
The population density question is one he hasheard often from municipalities hesitant to open injection sites.
"Certainly for a long time, we heard from people in Toronto, 'the problem is not like Vancouver, it's not like the Downtown Eastside, there are people spread out through the suburbs, so I don't think Insite is the best model.' And that may be true. A freestanding structure like Insitemight not be the right solution for everybody.
"However, what we've learned over the past 10 yearsis there's a variety of different ways to implement supervised consumption services in ways that make sense for the local community."
Milloysaid pop-up sites and smaller sites that have only one or two booths at existing health centres may be a better model for Winnipeg.
Toronto responds to crisis
Despite initial hesitancy, Toronto is the latest Canadian city to open supervised injection sites.Toronto Public Health hasopened three sites over the past six months, two of them permanent. The other is a temporary or "pop-up" sitethat will move as needed. Toronto also hadan unsupervised safe injection site.
Toronto has seen a rising number of overdose deaths, said Dr. Rita Shahin, associate medical officer of health for the City of Toronto. While she said the city and the province are looking at a number of different ways to help, including more prevention programs and treatment, supervised injection sites were needed to save lives immediately.
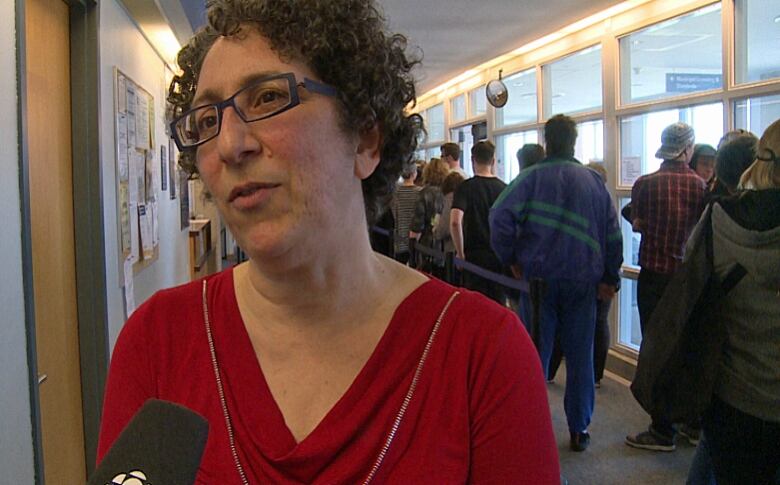
Shahin said the city was deliberate about where they opened their sites, adding that people "would not travel long distances to use the supervised injection sites."
Since opening in August, about 2,000 people have used the Toronto sites, said Shahin.
"We've definitely been able to respond to people who've overdosed. There have been over 30 overdoses in the facility since we opened. And we've also provided additional services in over 1,200 of the visits to the facility."
Province is reacting: Pallister
Manitoba has taken some steps andis currently developing a strategy to help deal with the province's addiction crisis, said Premier Brian Pallister, but he added root causes need to be targeted as well.
"Too often I think I've seen in the past[governments] often throw significant resources at the problem, but they too often do that without addressing cause and effect.
"So we want to balance our investments to make sure we're addressing both the causes as well as the reality of the challenges that we face today as a consequence of this drug problem."

In addition to resources, more co-ordination is needed between agencies, added Fry.
"Not only addictions and mental health, but also law enforcement. And several years ago when crystal meth did hit a peak in Manitoba, there was in fact a task force established.
"So it may very well be something that is required right now in Manitoba to actually establish that level of response."
Dr. Milloy called addiction and overdose deaths one of the leading health crises of the decade.
"In terms of overdose, I'm happy to report that none of the thousands of overdoses which have occurred in the [Insite] facility have ever resulted in a fatality. We also found that using the facility was also strongly associated with HIV prevention practices," with users 70 per cent less likely to shareneedles.
"Wealso found it was strongly associated with people accessing care for addiction, including going to rehab, going to detox, and starting methadone maintenance therapy."
The site was also associated with a significant decline in drug paraphernalialitter on the streets, and brought no increase in crime, saidMilloy.
Shahinsaid they have also not seen an increase in crime in Toronto areas near the sites, either.
The B.C. Centre on Substance Use, whereMilloy currently works,has recently published guidelines for municipalities that want to explore opening supervised injection sites, he added.
"Safe injection sites are no panacea and they're no magic bullet," he said.
"However, the scientific evidence is clear that they are an effective part of an evidence-based response to the risk of overdose, to HIV, and other drug-related harms."











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)