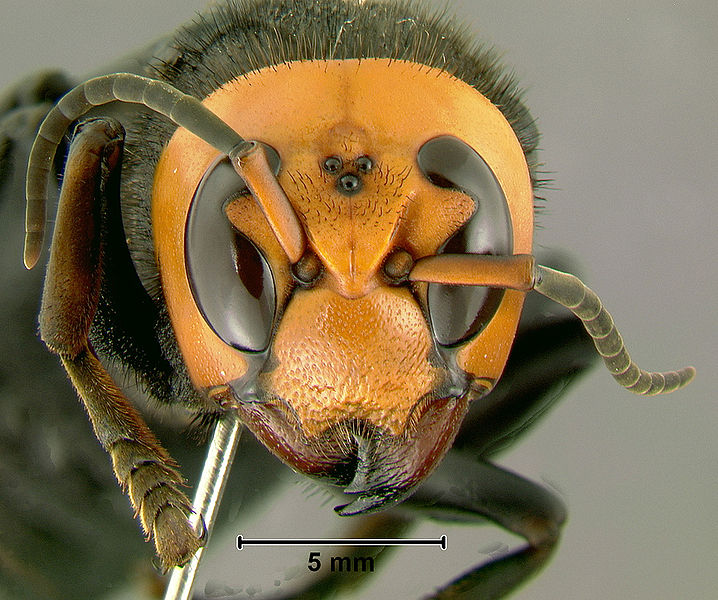
Zika virus risk low but spooks Manitoba travellers
Most infected with Zika will have no symptoms, still no definitive proof virus causes birth defects
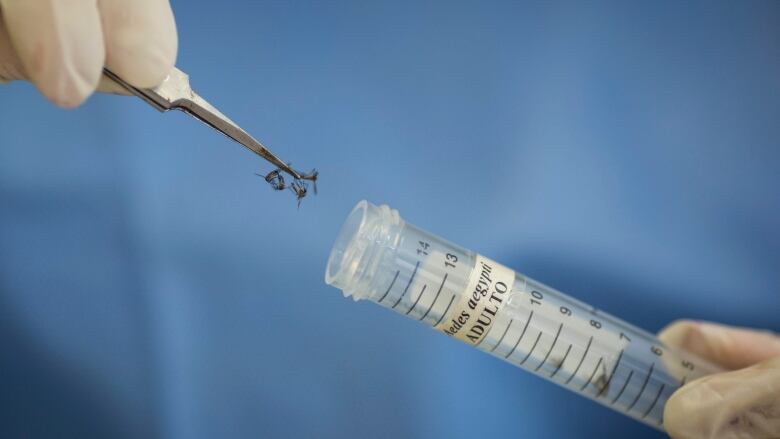
SomeManitobansarecancelling their holiday plans over fears of the Zika virus.
Three families who booked vacations with CAA Manitoba said the virus was a reason for cancelling their trips, said a CAA spokesperson Thursday. All three familieswere expecting a child.
But there are still many unknowns when it comes to Zika, including whether a disturbing increase in birth defects in Brazil should be blamed entirely on the virus,say two public health experts.
"The real problem is we don't have enough solid science to be able to determine the true risk," said Dr. Richard Rusk, medical officer of health for communicable diseases with Manitoba Health.
- Air Canada to give refunds or let passengers change flights over Zika virus concerns
- Zika virus outbreak emergency meeting called for Feb. 1, WHO chief says
Last year, the Zika virus was reported for the first time in many popular vacation spots for Canadians,including Mexico and other countries in Central and South America, said the Public Health Agency of Canada.
On Thursday the World Health Organization (WHO) Director General Dr. Margaret Chan described the Zika virus as "spreading explosively," at a special meeting on Thursday and said the "the level of alarm is extremely high."
Brazil's Ministry of Health recently drew a connection between women infected with Zika during pregnancy and microcephaly or an underdeveloped brain in their babies.
The normal rate of reported microcephaly in Brazil is about fiveper 100,000 live births and considered "quite rare," said Dr. Joel Kettner, medical director of the International Centre for Infectious Diseases and associate professor at the University of Manitoba.
In 2015 the rate went up 20-fold, to 100 per 100,000 live births. While alarming, the figure could still be considered on the low side when it comes to abnormalities in newborns, he said.
- Zika virus: what you need to know
- Canadian Blood Services to defer donations from travellers to Zika areas
Among the general population, the risk of getting seriously ill from the Zika virus is also very low, said Kettner.
About 80 per cent of the time, people who contract thevirus don't experience any symptoms and for the 20 per cent who do, they fight it off within a week, he said.
Zika symptoms are somewhat similar to sunstroke, said Rusk, often including a skin rash and fever. Very few patients go on to develop any serious or severe disease, he said.
Zika among many risks to travellers
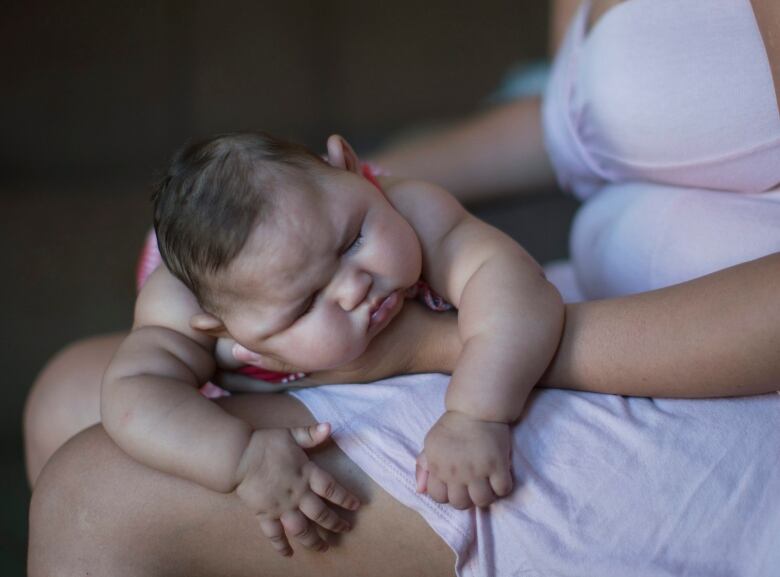

Long-time threats to vacationers, like dengue fever or malaria, should be also taken into account when making travel plans, he said. Both the infections can cause severe complications for adults and unborn children and are present in places like Mexico, the Caribbean, and Brazil.
Travel decisions need to be made in a context of trading off risks, Kettner said, and understanding how much of an additional risk Zika poses. Researchers, for example, do not yet know whether a woman has a greater chance of being in a traffic accident while on vacation than contracting Zika and seeing her child born with microcephaly, he said.
Rusk, with Manitoba Health, nevertheless recommends women who are pregnant or who are planning to become pregnant consider avoiding areas where high numbers of people are infected with Zika.
He suggests people consult the Public Health Agency of Canada website or the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to find out where the latest Zika hotspots are. If Manitobans chose to travel regardless of the risk, he recommends they take normal precautions to avoid mosquitobites, like using insect repellent andavoiding the outdoors when it's buggy.
And in case Manitobans were left wondering, the likelihood of mosquitoes carrying Zika virus making their way to Canada is "next to zero," Rusk added.
Public Health Agency of Canada publishes thetravel risks for all countries. To see the latest level of concern related to Zikavirusvisit their website.
- Level one:Practise usual precautions
- Level two:Practise special precautions
- Level three: Avoidnon-essentialtravel
- Level four: Avoidall travel











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)