These are all the hurricanes that hit Canada since 1900
By the time they reach us, most hurricanes are weakened post-tropical storms
This year's hurricane seasons has wrought destruction onthe Caribbean and the United States, but Canada hasexperienced almost nothing like its southern neighbours.
The northern climateshields the country from the brunt of tropical storms.
But not always. Since 1850, Canada has been hit by 240 hurricanes, according to data from the U.S. National Oceanic and AtmosphericAdministration. That's about one or two per year, on average.
This may seem like a lot, but not if you consider that more than 2,100 Atlantic and Pacificstorms were recorded since then.
The map below shows 163 storms that made landfall in Canadabetween 1900 and 2014.
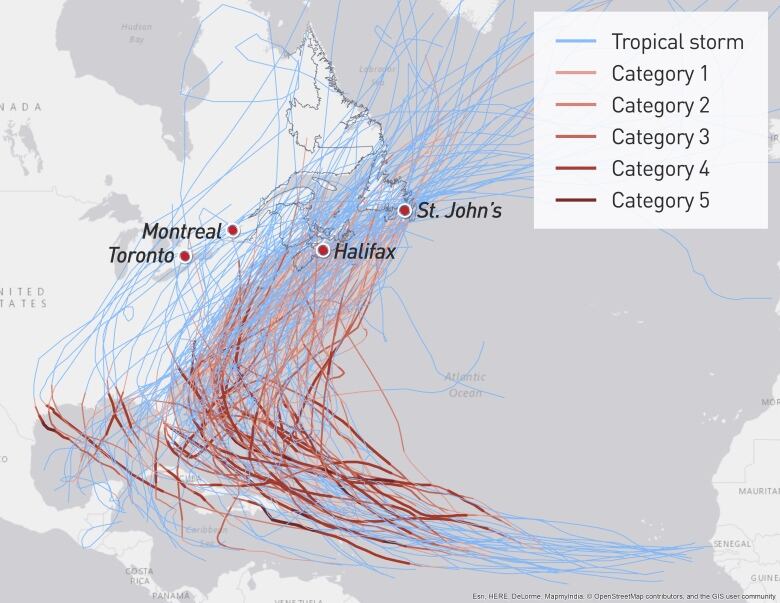
Most of the hurricanes haveone thing in common: by the time they reached Canadian soil they weren't really hurricanes.
"By the time that these hurricanes do impact Canada it's mostly a huge rainstorm and not much of a windstorm," Athena Masson,a meteorologist and PhD candidate at the University of Toronto, told CBC Radio'sQuirks and Quarks.
"So Canada will not really see Category 4, Category 5, or the wind speeds that we've seen with Hurricane Harvey as it came ashore."
The chart below shows the wind speeds of all the hurricanes that touched Canada since 1975.

Most hurricanes that touch the Canadian landmass have been downgraded to post-tropical storms, meaning they are no longer driven by warm ocean temperatures, but rather by northern weather systems. Most make landfallwith an average wind speed of 30 km/h (true hurricanes spin at 119 km/h or more).
But they can pick up speed again, according to BobRobichaud of the Canadian Hurricane Centre.
"Post-tropical storms have a clear distinction between rain and wind. Usually you'll have rain on the right sideof the track, andwind on left side," Robichaud said.
In rare occurrences every three or four years, Robichaudsaid hurricanes maintain their tropical strength when they reach Canada.
Among the deadliest was Hurricane Hazel, in 1954. By the time it reached Canada had become an extratropicalstorm, but it still resulted in the death of 81 people, mostly in Toronto.
Hurricane Juan in 2003 was the most destructive wind-heavystorm in recent history. It whipped through Halifax as a Category 2 hurricane with winds speeds reaching160 km/h. It claimed eight lives, flattened forests, and caused more than $100 million in damages.
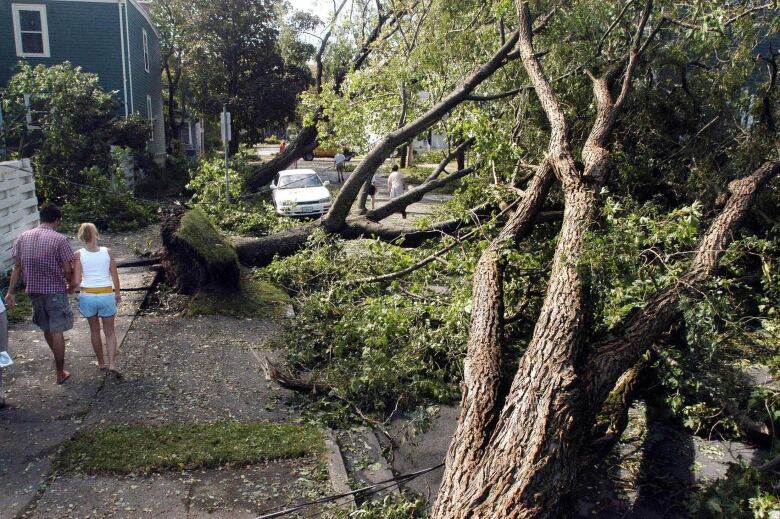

Then, in 2010, Hurricane Igor struck Newfoundland, but it was mostly a rainy event, albeit a deadly one. An 80-year-old man was killed after he was swept into a rain-swollen river.
"It put most of the island on therainy side of storm. There wasflooding, road washoutsand a recovery that took weeks," he said.
Hurricane Irene in 2011 showed that rain-heavy storms can also wreak havoc inland, not just in the Maritimes. It slammed Quebec, flooding roads and downing power lines.
And if it seems from the chart above that hurricanes have been getting more frequent, they have, but only because we're in an active period of hurricane activity that started in 1995, according to Robichaud.
"These active periods last on average 20-30 years," he said.











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)