Judge at Dennis Oland murder trial is a leading legal expert in DNA
Justice John Walsh was among first lawyers to use DNA evidence in 1991 case of serial killer Allan Legere
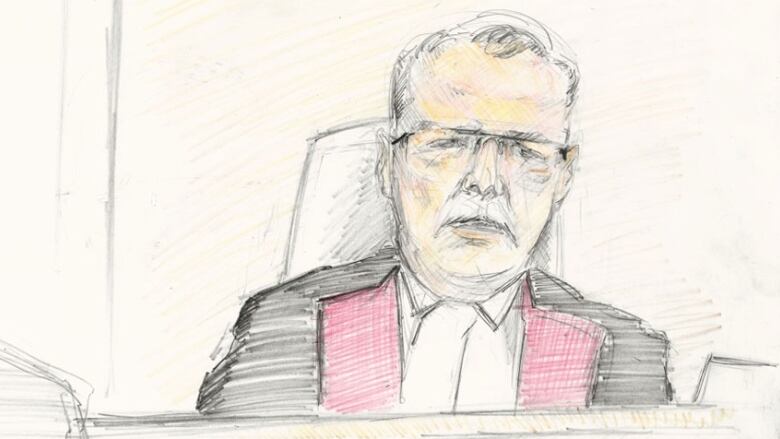

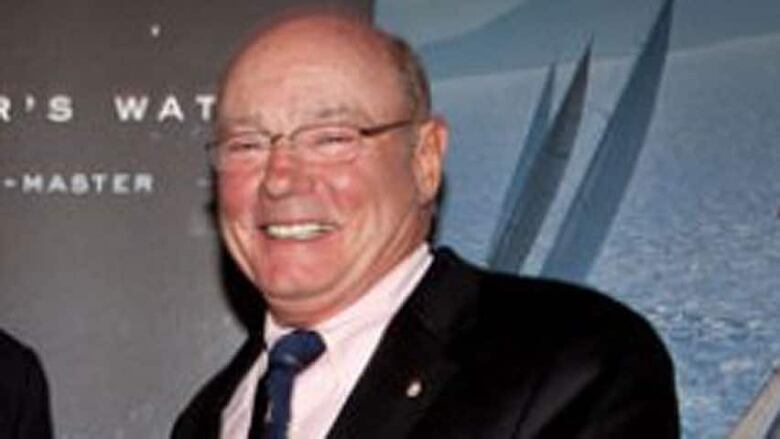
The judge presiding over Dennis Oland's second-degree murder trial in Saint Johnis one of the country'sforemost experts in the legal application of forensic DNA typing.
- Dennis Oland's defence abruptly closes case in murder trial
- Dennis Oland concedes inconsistencies between testimony, police statement
- Dennis Oland tells murder trial he didn't kill his father

Legere, an escaped convict who went on a seven-monthkilling spree in 1989, was convicted in 1991of four counts of first-degree murder.
Walsh was part of the prosecution team that secured convictions in all four cases, due, in large part, to the DNA evidence.
The RCMPforensic lab foundthere was only one chance in 310 million thatsomeone else would match the genetic codes taken from semen samples atthe murder scene of sisters Donna and Linda Daughney, and a one in 5.2 million chanceat the scene where an elderly woman, Annie Flam,was killed. There was no DNA found at the murder scene of priest James Smith.
Legere unsuccessfully appealed in 1993 and was subsequently declared a dangerous offender, a designation that allows for permanent incarceration.
Dennis Oland is accused in the 2011 bludgeoning death of his father, prominent businessman Richard Oland.

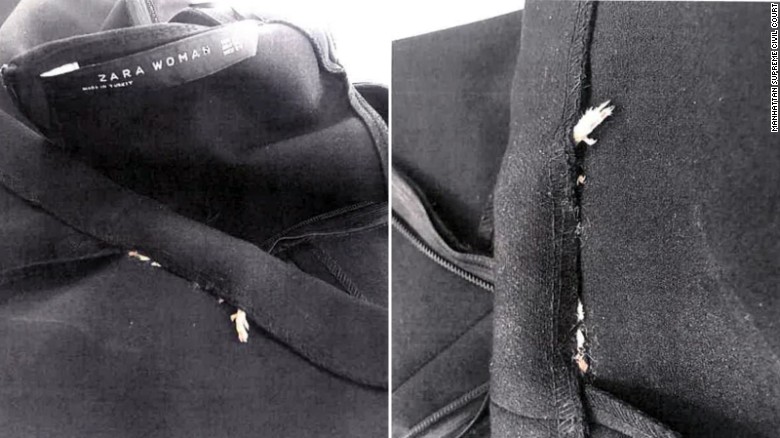
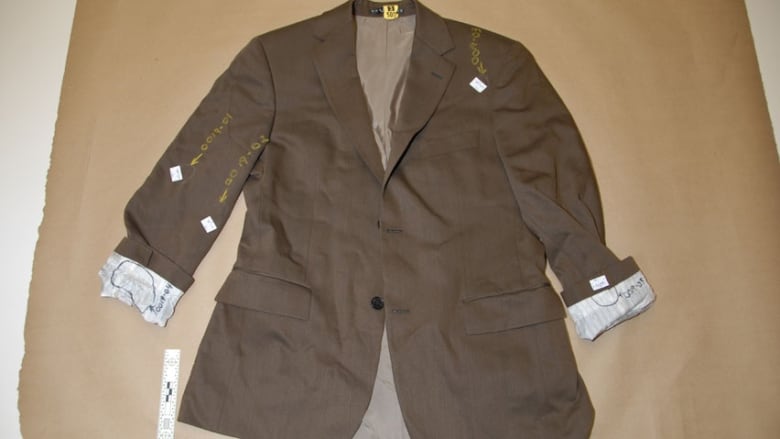
The jacket had three small bloodstains on it on the right sleeve, upper left chest and on the back and the DNA extracted from those areas matched his father's profile. The chances of it not being the victim's DNA are one in 20 quintillion, a DNA expert has testified.
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid,is thegenetic coding found incells.
Oland, 47, was the last known person to see his father alive during a meeting at his investment firm office on July 6, 2011.
The body of the69-year-old multimillionairewas discovered lying face down in a pool of blood on hisoffice floorthe following morning. He had suffered45 sharp and blunt force injuries to his head, neck and hands. No weapon was ever found.
Walsh, who was brought in from Miramichi to hear the high-profilecase,is expected to begin giving his instructions to the jury early next week.
He warned the jurors it could take him up to two days to do so.
Input on DNA warrant and data bank legislation
Walsh was appointed to the Court of Queen's Bench in September 2009, less than a year after being appointed a provincial court judge.
In 2003, while a Crown prosecutor, he received one ofthe Canadian Bar Association's most prestigious awards the JohnTaitAward ofExcellence, which honours, recognizes and celebrates accomplishments of public sector lawyers.

In 1998, Walsh was invited to address the federal Standing Committee on Justice and Human Rights on DNA-related legislation. He had authoreda public consultation paper in 1994, which formed the basis for the federal DNA warrant legislation and DNA Data Bank legislation.
Walshhad been seconded to the federal Department of Justicecriminal law branch the previous yearand worked exclusively in thearea of forensic DNA evidence.
He contributed articles and book chapters to legal and scientific publications alike, and offered consultation to police and prosecutors on some of the most serious crimes.
Walshwas admitted to Queen's counsel in 2001. He became a Crown prosecutor in 1987, after practising general law for about a decade.
Walsh, who was born and raised in Miramichi,became a member of theNew Brunswick bar in 1977, the same year heobtainedhis law degree from the University of New Brunswick.
He previously obtained a bachelor of arts degree from St. Thomas University.











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)