Give some First Nations schools more money than urban counterparts, says federal minister
'Thats music to our ears': Assembly of First Nations' education chair Bobby Cameron

FirstNations schools deserve the same level of funding as those in Canada's cities and towns, but some First Nations schools should get even more, saysMinister of Indigenous and Northern Affairs Carolyn Bennett.
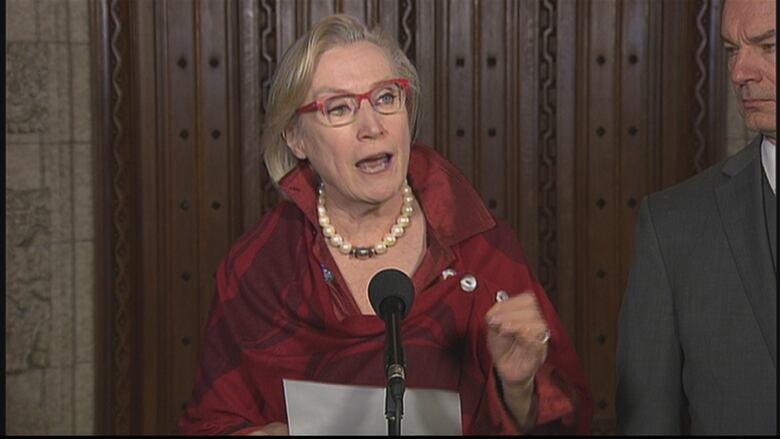

In an interview with CBC News, Bennett noted that many First Nations schools are remote. Some would like to develop and teach Indigenous language curriculum. Others want to integrate cultural camps or "on-the-land" learning into the school year.
These and other considerations will require more money than the average urban school, Bennett said.
"That's music to our ears," said Assembly of First Nations regional chief and education chair Bobby Cameron.
Cap leads to gap
The funding gap between schools on and off First Nations has been growing for decades since the federal government imposed a two per cent "cap" on education increases to schools and other services on reserves.
Both Liberal and Conservative governments maintained this cap.
Meanwhile, provincially funded schools in cities and towns received far bigger increases to cover teacher salaries, basic inflation and other costs.
- Federal funding gap disadvantages First Nations students, PBO says
- First Nations education a cash-strapped 'non-system,' bureaucrats tell minister
As a result, many First Nations schools can't afford computers, science labs or sports equipment. Teacher turnover is often high because salaries aren't competitive. Only a handful of schools offer Cree, Dene or other immersion programs, even though urban students across Canada have ready access to French immersion and other language instruction.
Some schools are succeeding in spite of the situation. The Island Lake First Nation School, located in northwest Saskatchewan near the Alberta border, has enough computers, and many students are thriving, said principal Jon Kemp.
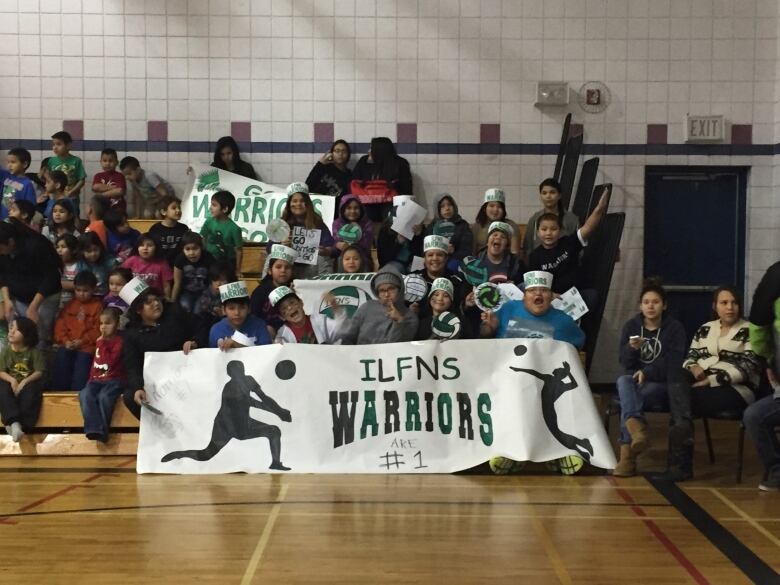

But they have few social workers or other specialists that are needed, Kemp said.
He saidelders and teachers are doing their best to teach Cree culture, but more funding would allow them to offer a full immersion program.
"We have students that struggle," he said."These other supports would be great."
Beyond parity
TheTrudeaugovernment haspledged to remove the funding cap and give $2.6 billion over five years for First Nations education. That will partly close the funding gap facing the 515 elementary and high schools on reserves.
- $2B needed for 'immediate' fixes to First Nations schools, bureaucrats say
- Liberals given plan to roll First Nations education money out faster, but decided not to
Bennett now saysthe goal is to go beyond parity for First Nations school funding, and alsoto allow Canada's First Nations to implement their own beliefs and traditions into their school systems.
"We've got a ways to go [but]I think we're going to do it," she said.
She emphasized "First Nations-led systems that actually set their own priorities and get funded according to their need."
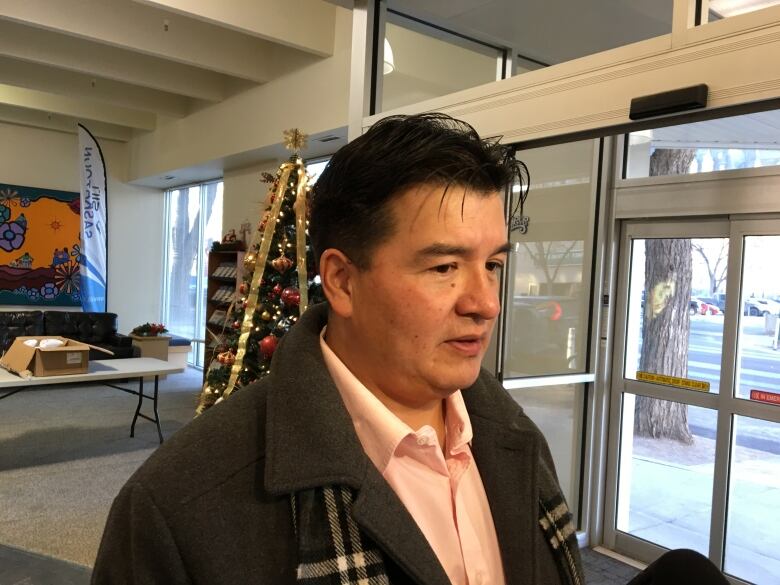

Cameron lauded Bennett for thefunding pledge and said he is happy to hear her say publicly what she recently told the Assembly of First Nations and other leaders.
Healso appreciates the priority Bennett is placing on First Nations' control of their own education.
"It's been a long time coming where we've had a serious investment into First Nations education," Cameron said. "I mean, we're talking about two, three, four decades herewhere our First Nations leadership and students and post-secondary students have been waiting patiently."
He expects more progress when Bennett meets with him and other leaders in February at a Calgary forum for First Nations directors of education.











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)