After wet summer, 'savour the joy' of increased numbers of monarch butterflies in Toronto
Rainy weather means more flowers to fuel insect populations in the city
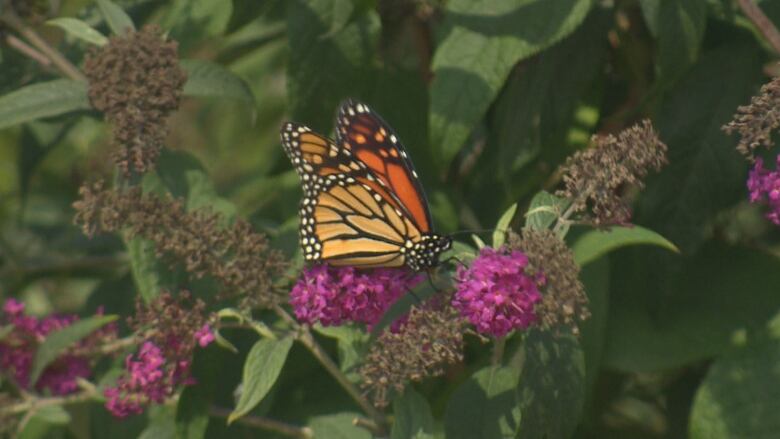

One of Canada's most cherished species seems to be making a comeback in Toronto gardens at least for a few more days.
Monarch butterfly watchers in Canada and in the United States say it's been a good year for the iconic orange-and-black pollinators, wholeavefor winter habitats in Mexico from Canada and the U.S. in September, arriving at their destination about a month and a half later.
- Monarchs make the most of a mild summer, biologist says
- Project aims to make Toronto more butterfly friendly, 1 wildflower patch at a time
Jode Roberts, who manages the Butterflyway Project for the David Suzuki Foundation, told CBC Toronto it's been a "crazy great summer" for monarchs, thanks to a successful migration back from Mexico and theaverage temperatures and wet weather Toronto experienced over the summer.
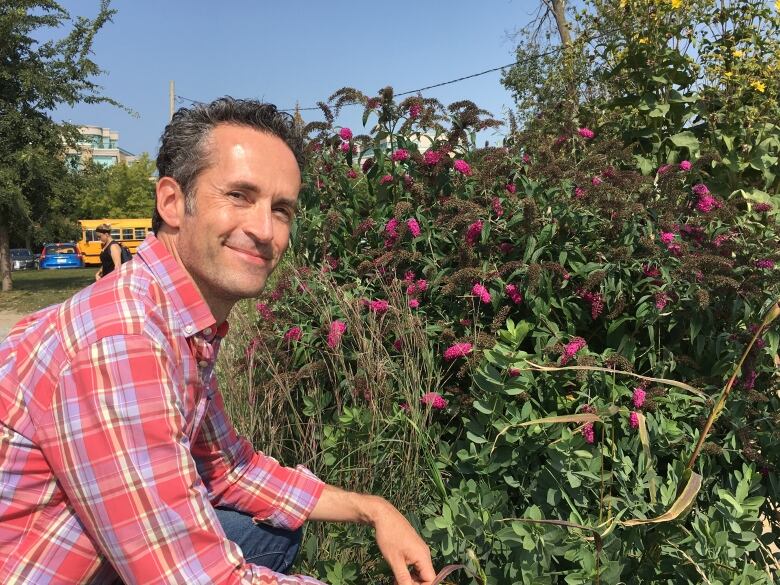

"When there's lots of rain, that means there's lots of nectar" for the monarchs to chow down on, he said.
Roberts also credits a David Suzuki project introduced a few years ago to encourage Torontonians to plant monarch-friendly plants like milkweed, saying that "what we are seeing this summer is, I hope, the result of that work by citizens."
Monarchs are currently considered a species of "special concern" by Ontario, but Roberts said his organization is pushing for better protections.
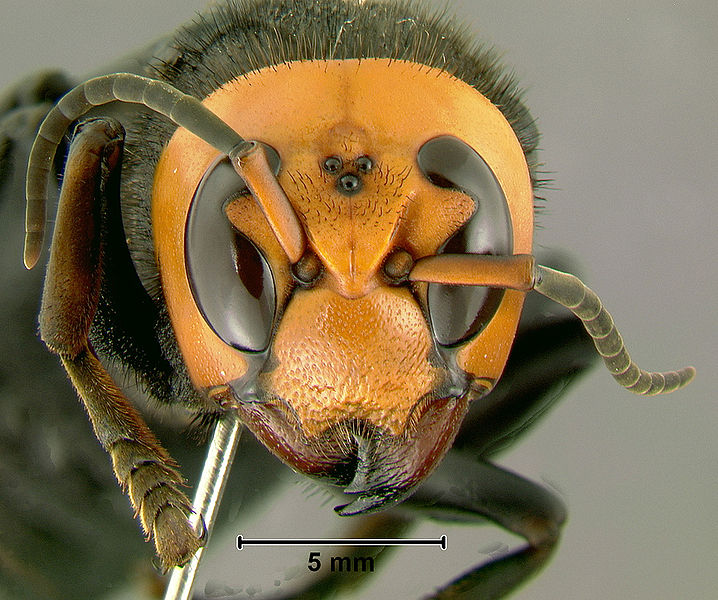
Boost for wasps and bees
The mild weather, andwildflowers that have flourished thanks to plenty of water, havehelpedother species as well some welcome, some less so.
"Wild bees and butterflies all benefit," said Roberts, noting that there are more than a hundred species of butterfly in the city, including the painted lady, an orange and black butterfly often confused with the monarch.
Many Torontonians have taken to social media to describe anotherslightly less welcome visitor: wasps.
Scott MacIvor, an assistant professor of biological science at the University of Toronto in Scarborough who studies wasps and bees in the city, makes a case for why that's good news as well.
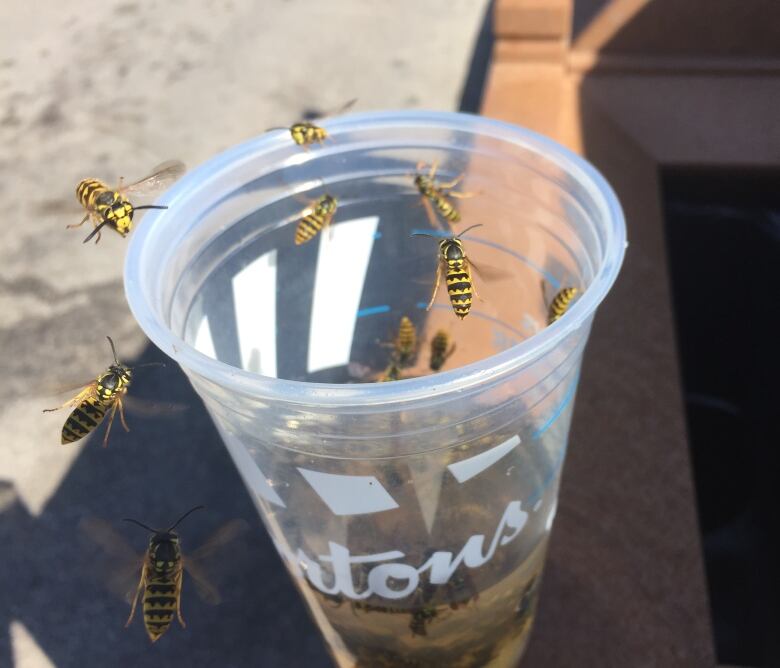

"Wasps play really essential roles as predators and pest-controlling agents in our environment," he said. "For every super-abundant spider or aphid there's a wasp for that."
Though the monarchs are now beginning their migration"with a little bit of wind and good luck," as Roberts puts it, other insects will likely stick around as Toronto continues to experience a streak of warm weather.
"I would say we'll be seeing bees and wasps well into October," said MacIvor.
Slow recovery from population crash
In the meantime, Roberts says the city should "savour the joy" of the monarchs, especially given their difficult past few years.
"In the 1990s, there were about onebillion monarchs, and that number dropped by 95 per cent four years ago," he said.
Improvements have been slow since then, with habitat destruction and severe storms imperiling the butterflies as they make the long journey to and from their winter homes in Mexican forests.
"Lighter than a paper clip and they fly 4,000 kilometers they're really at risk to any slight changes in the climate or the geography they're going through," said Roberts, pointing out that single storm in Mexico last winter killed 10 million monarchs.
Don Davis, a citizen scientist who has kept an eye on monarch populations in Ontario since 1967, told CBC Toronto in an email that monarch populations this year seem to be "doing well," with July 1butterfly counts showing an increase in the population.
Chip Taylor, director of Monarch Watch at the University of Kansas, wrote in a late-July blog post that "it looks to be a good year for monarchs," though the best gauge of how good will come when the butterflies land in Mexico, where they can becounted more thoroughly.
Torontonians who want to help monarchs continue their rebound can plant local wildflowers and milkweed, said Roberts, pointing out that a thriving flower garden has the added benefit of helping a clutch of other pollinators as well.












_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)