Scientists call for tri-national conservation effort to save monarch butterfly
'This population is in real trouble,' lead researcher of study into monarch butterfly birthplaces says
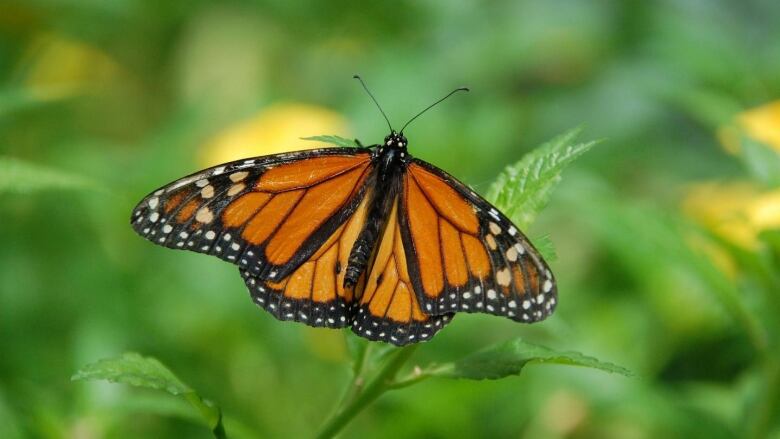

Researchers from the University of Guelphhave helped pinpoint locations of monarch butterfly breeding grounds with the hope of a multi-national conservation effort.
During their migration, monarch butterflies travel from Mexico into southern Canada, a journey of about 5,000 kilometres annually. However, over the past 20 years, the monarch population has seen a precipitous decline, with numbers falling by about 80 to 90 per cent,the researchers say.
Much of the blame for this has been attributed to the loss of habitat, more specifically, the loss of milkweed plants. There is concern that the species could be lost entirely if the trend continues.
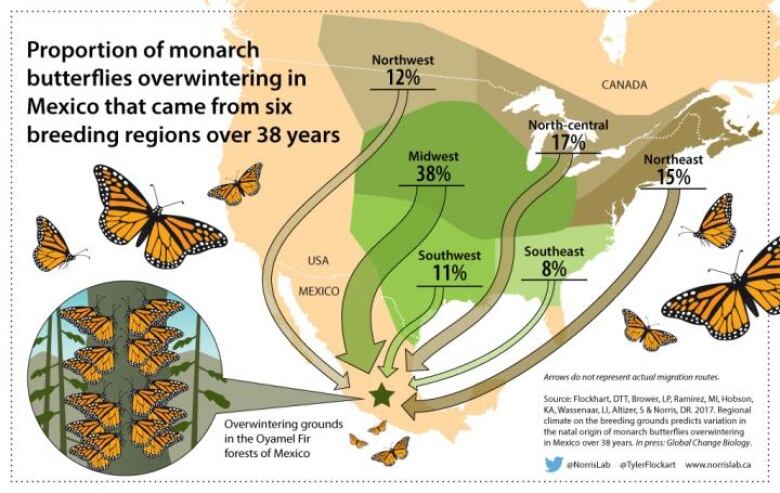
In an effort to determine where conservation efforts would best be focused, the Ontario-basedteam studied wings of butterflies collected as farback as the mid-1970s.
The researchers had expected to find that the breeding locations for mostmonarchs would be in the U.S. Midwest.
It's a chain system and if any of these linksin the chain falls apart, then the whole thing will fall apart.- Tyler Flockhart, University of Guelph
But chemical analysis of the butterflywings found that just 38 per cent bred in that region.
What all of this means, the researchers believe, is that there needs to be a large-scale plan to save the monarchs, which take part in amigration so long it can take multiple generations to complete.
"When we're talking about monarchbutterflies, we're talking about conservation actions that need to happen across three different countries," said Tyler Flockhart, lead author of the study, whichappeared in the journal Global Change Biology.
"Because the butterfliesthat arrive in Canada are not born in Canada;they are born in the United States.And the butterflies born in the United States are the ones that come from Mexico. It's a chain system and if any of these links in the chain falls apart, then the whole thing will fall apart."
According to WWF Canada, illegal logging and climate change are also contributing to the loss of monarchs: as the climate changes, weather conditions in both their Mexican wintering location and summer breeding grounds are affected.
In 2016, monarchs made a bit of a comeback, covering about four hectares in their wintering grounds in the mountains west of Mexico City. That's compared to 1.13 hectares in 2014 and a record low of 0.67 hectares in 2013.
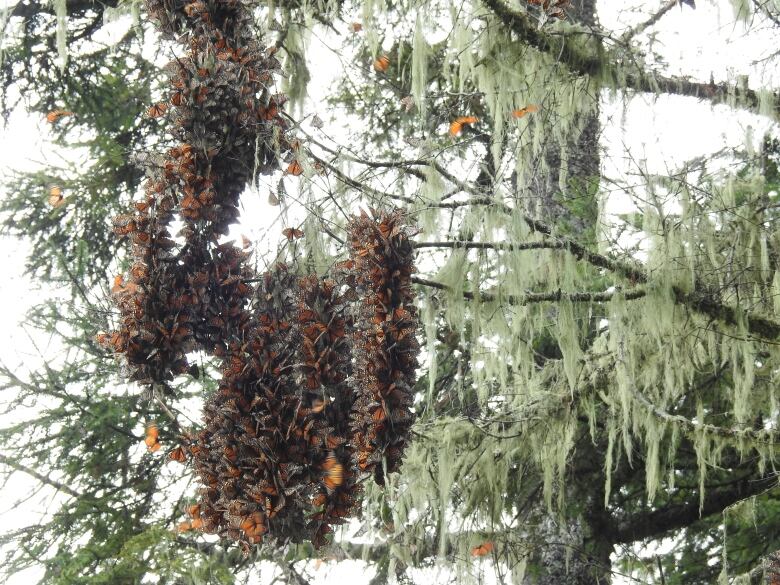

The samplesthe researchers used were provided by Lincoln Brower of Sweet Briar College in Virginia. Brower has collected samples of butterflies for the past 50 years, and Flockhart saidthey wouldn't have been able to conduct the study without the vital historical collection. He'd like to see scientists from all three countries begin to collect samples of monarchs annually in order to get a consistent picture of the monarch's welfare.
"We need to collect these types of samples every winter," Flockhart said. "Particularly if we'regoing to spend millions of dollars to conserve this species."
"This is real," Flockhart said."This population is in real trouble."
With a file from The Associated Press











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)