Where the lopsided economic impact of COVID-19 in Canada goes from here
The economic effects on Canadians have varied wildly: Some are thriving while others are trying to hold on
All economic downturns are unfair. Some people inevitably get hit harder than others. But almost a year into the COVID-19 catastrophe, the data makes it abundantly clear:the impact of this crisis is uniquely unequal.
More than a million Canadians remain under- or unemployedwhile millions more simply adjusted to working from home.
The second wave of COVID-19 cases and increased restrictions in many parts of the country have clobbered the most vulnerable workers who were already struggling. But many Canadianswho were lucky enough to keeptheir jobs have been able to cut expenseson travel, commuting and child care. In doing so, they've saved more than $170 billion, collectively.
Stock markets have soared to all-time highseven while the global economy collapsed. Since bottoming out last April, both the Dowand the S&P are up more than 60 per cent.
Djenaba Dayle lost her job as a server at events in Toronto when the pandemic hit last March.
"You watch the news and you see people who are privileged and fortunate enough to be in a position to save money right now," she said. "And I know that, for myself, it's just debt."
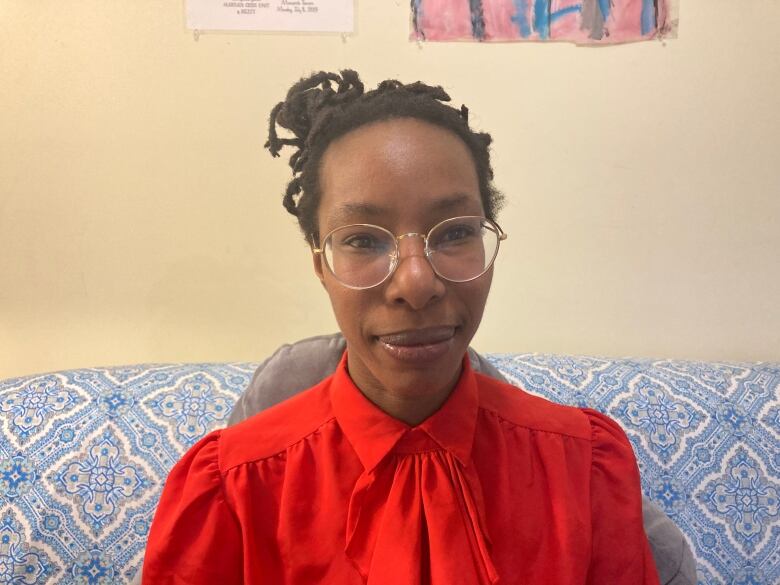

When COVID-19began spreading last year, Dayle knew tough times were coming. She applied for the Canada emergency response benefit (CERB) and eventually the new extended employment insuranceprograms. But it's still not enough, she said.
"It's either pay my full rent and not eat or eat and get behind in my rent."
On the other side of the country, Cole Westersund has experienced both sides of the pandemic'seconomic divide. Last March, he was terrified that his work as a real estate agent in Vancouver would grind to a halt along with the rest of the economy.
"It was incredibly difficult to face the fact that you might not be able to put food on the table," he said.
Then, about a month into the pandemic, some restrictions began to lift. And suddenly his phone started ringing, he said. Clients were looking for properties out of town.
"Coming out of the lockdown, they figured, 'Hey, we have this money saved up,'" saidWestersund. "If people were fortunate to keep their jobs, [they figured]let's change our lifestyle. You know, if you're a skier, if you're a hiker, a biker or a fisherman."

He saidpeople were looking for more space andprivacy or even just a break from being cooped up because of public health restrictions.
And business has been booming ever since, he said. He'sbeen struggling to keep up with demand. The sale of recreational real estate, such as cottages, has soared 11.5 per centin the first nine months of 2020.
But Westersund said it's important to rememberevery purchase is also a sale. And many of the clients selling their properties were listing because times were sotough.
"Stepping into a client's house, knowing full well that the reason that they're selling is because they need the money, it's a difficult conversation to have," he said.
It is the definition of a K-shaped recovery.People on the lower branch have seen their fortunes fall and have not yet recovered while those on the upper branch have prospered.

Experts worry the increased division between those two branches may outlast the pandemic.
"Some of these effects could end up being permanent, and the bottom part of the K could persist for quite a while," saidformer Bank of Canada governor Stephen Poloz, speaking at an online event onJan. 13hosted by Western University'sIvey Business School.
The concern is that theworsening inequality of the economic downturnwill lead to what economists call scarring:long-term job losses that result in lower growth and drag the whole economy down.
Poloz saidthe key right now is to support Canadians who are still reeling financially. He pointed out thatinterest rates remain at historic lows.
"The main thing is for us to focus on boosting growth," he said. "I'm hopeful that, in this context that we find ourselves, we can have more federal and provincial collaboration that allows us to do some things that will boost growth forever."
WATCH | Canadian entrepreneurs on navigating the pandemic:
Djenaba Dayle, the server from Toronto,takes umbrage with the term scarring.
"They're deep, festering, open wounds," she said. "It's not a scar. Things have not healed over."
In order to heal, she said,Canadians need to rethink how social programs work. Dayle saidthe COVID-19 crisisis a glaring reminder that the support system wasn't adequate before the pandemic hit.
"[We need]changes to EI, changes to how we approach people who are renters, changes to how we support folks who are down on their luck," she said.
Dayle saidthe minimum wage needs to rise,and thatrent control is crucialand not just during a crisis. Several economists have proposed introducing automatic triggers that would restart more intensive support programs such asCERB when major trouble hits.

On the upside, most experts agreethe recovery is nearly here. Daily COVID-19 case numbers are finally starting to decrease. Vaccines are beginning toroll out, albeit slowly. Economic forecasts from the major Canadian banks suggestblockbuster growth in April, May and June. Even once you factor in a negative quarter of growth to start the year, economists are predicting GDP will come in around 4.5-5 per centfor 2021 and at a similar level in 2022.
"It's a massive acceleration of growth that we're expecting over the next couple of years or so," saidDerek Holt, vice-president and head of capital markets economics withthe Bank of Nova Scotia.
It's been decades since Canada has seen that level of growth. Growth like that means investment and building and that means jobs will be created. It means everyone benefits.
Butwill Canadians remember how much people needed government assistance during the worst of the pandemic? Will they remember how insufficient it was for many?
Dayle isn't sure
"Let's say I have very little faith," she said. "But [I have]a great deal of hope."













_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)