La Nia weather pattern could ease B.C.'s ongoing drought
Dry conditions have caused wildfires to burn year-round and water rationing in some communities
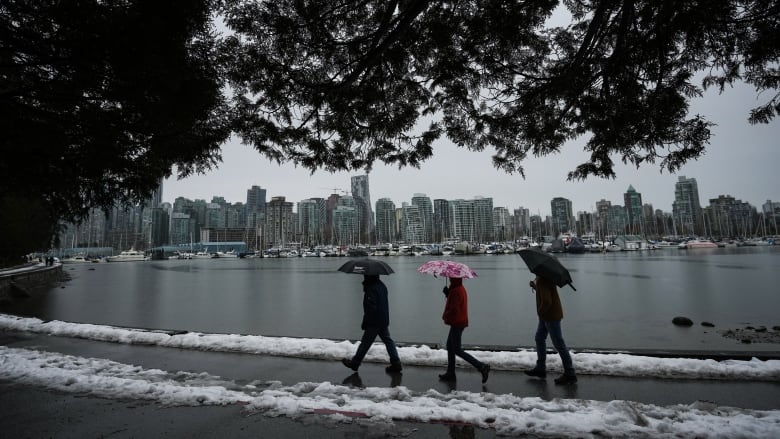

BritishColumbia'songoing drought could be eased by an expected La Nia weather pattern that would bring a colder and wetter than normal winter, an atmosphericsciences expert says.
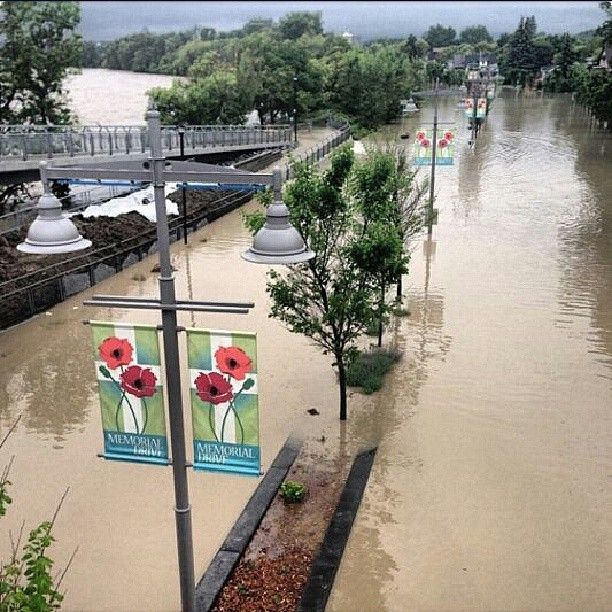
The prolonged drought has caused wildfires to burn year-round, forced some communities to ration water supplies and dangerously lowered water levels in rivers, affecting salmon runs.
Citing the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Sean Fleming, an adjunct professor of atmospheric sciences at UBC, said early projections show a 71 per cent chance that aLa Nia weather pattern will move in.
La Niais a climate phenomenon resulting from the flow of warmer water in the Pacific Ocean that typically brings lower temperatures and higher precipitation.
If those projections are accurate, that could help to "undo some of the persistent drought conditions," said Fleming, who works in UBC's Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences though it would also increase the risk of flooding and power outages.
"Potentially, we could be looking at greater than average flooding this winter if the La Nia conditions pan out," he said in an interview. "That also means, though, greater water supply, greater snowpack in general, greater water supply availability for the next spring and summer."
It could also bring higher hydroelectric power generation potential, he said, as well as stormier weather that might bring down power lines.
The latest available data from the province's drought information portal shows that, as of last Thursday,B.C.'s northeastern corner remains at drought Level 5, the highest possible ranking on the scale.
The River Forecast Centre and theB.C. Wildfire Service declined to comment on current conditions ahead of the provincial election, saying all communication will be "limited to critical health and public safety information, as well as statutory requirements."
B.C. Hydro spokespersonSusie Rieder said the power authority is urging people to be prepared for weather-related power outages ahead of storm season, as the multi-year drought has caused trees to weaken.
"Our meteorologist has been warning that, while drought levels have improved compared to last year, there's still that elevated risk of power outages in the event of a windstorm this fall," she said in an interview.
Rieder said that's especially the case forVancouverIsland and in northernB.C., which had several major wildfires this season.
"For places like the Lower Mainland and the southern Interior, drought stress has been a bit less, but trees and other vegetation are still at risk compared to a year with average precipitation," she added.
She noted that last year, following the worst wildfire season inB.C. history, the first windstorm of the season caused damage that left 235,000 customers without power.
TheB.C. Wildfire Service dashboard shows about 180 wildfires are still burning acrossB.C. A total of 19 blazes are listed as burning out of control. All but one are burning in thePrinceGeorgeFire Centre region, which covers the province's northeast quarter.
Fleming said scientists can often forecast weather about two weeks in advance and predict long-term changes in climate decades out.
"Seasonal to sub-seasonal forecasting is really hard," he said, adding that "no one really knows" with certainty what will happen this winter.
A La Nia event would have a series of cascading impacts, he said, but it is "impossible" to know at this point what will happen and if it would ease the multi-year drought.
"We won't know for a bit yet," he said. "But irrespective of that, if there's been a long, severe drought, and if that drought has managed to kill off a lot of vegetation, no matter what the winter is going to be like, you are probably looking at a higher than average probability of landslide activity."











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)