Firefighting turns to technology to get the jump on wildfires
Infrared scanners and computer modelling used to help battle blazes in Canadian forests

Wildfire ranger Dan Gorzeman directeda crew as itputout hotspotssmouldering beneath the boreal forest northeast of Slave Lake, Alta., in August 2015.
But he wasn'ton the ground.He washundreds of metres above the blackened bush inahelicopter,staring atthe screen of aninfrared scanner.
- Ideas|Listen to the wildfires documentary 'World On Fire'
- The science of how wildfires spread
- B.C. flight simulator to help firefighter pilots prepare for wildfires
"These scans show us where these ground fires are and we relay them on a map with co-ordinates," he said.
The ground crew can then take thoseco-ordinates and pinpointtheexact location of underground fires using GPS.
"The firefighters systematically go through and knock them off," Gorzeman said.
It's a one-two punch from the sky and the ground, allowing the crewto know for sure a fire is completely out so it canmove on with confidence knowingagust of air won't whip up the fire again.
Gorzeman says this is proven technology making a real difference in the wayfirefighters work in Canadian forests.
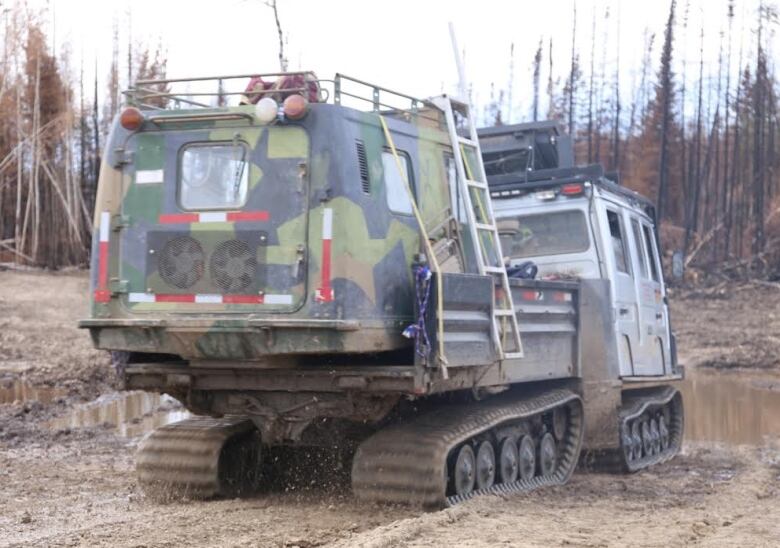

Another advance is how the ground crews gets around.To move long distances through the bush, they ride in something that looks like a tank.
Theall terrain carrier called aHgglund easily storesall the gear firefightersneed to tackle any situation andrumbles effortlessly on its hugetracksovertoppled trees, throughthickmud and streams.
Rain made to order
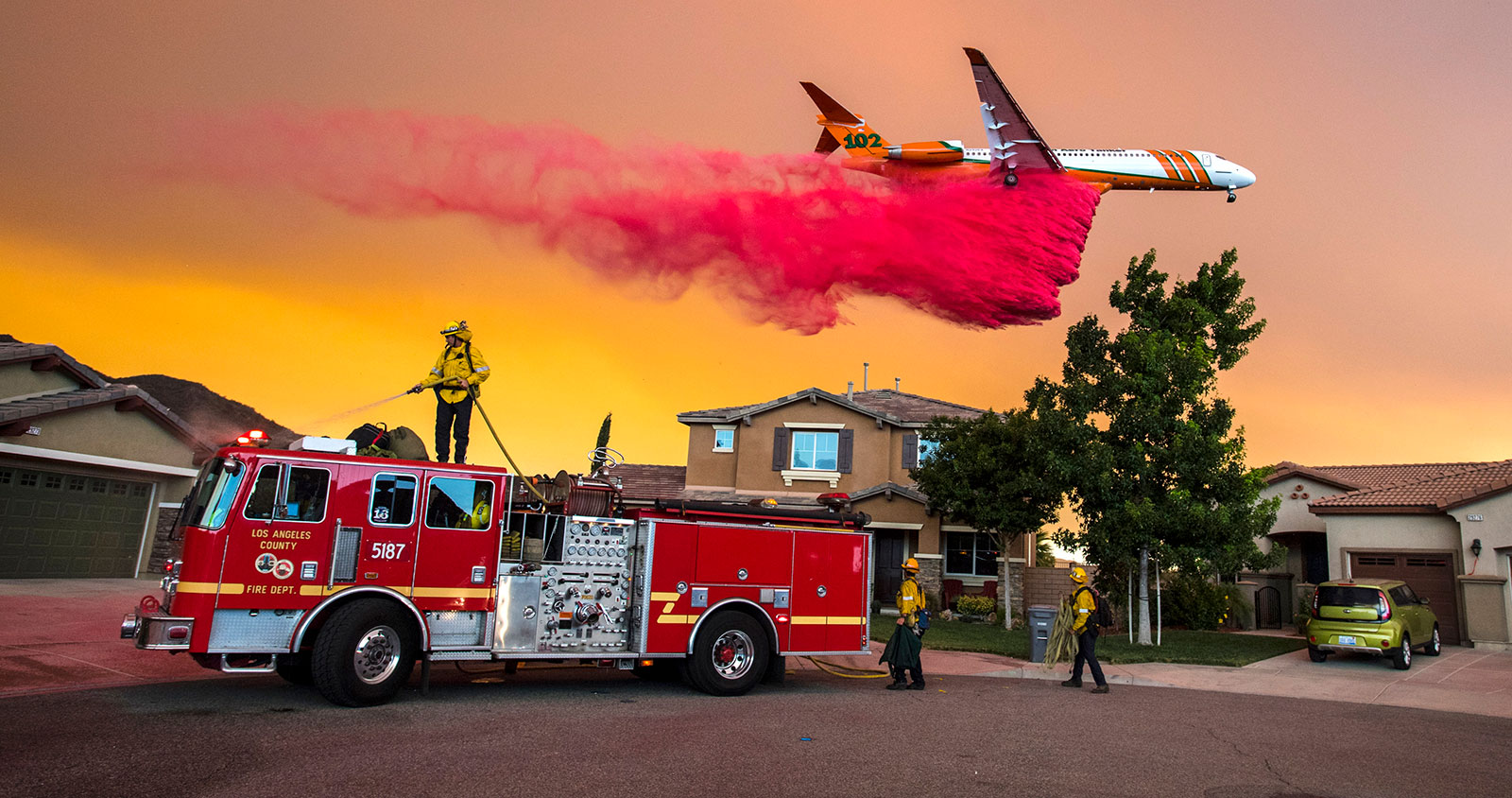
Whether you're protecting the bush or buildings, getting water on a fire is key to bringing it under control.
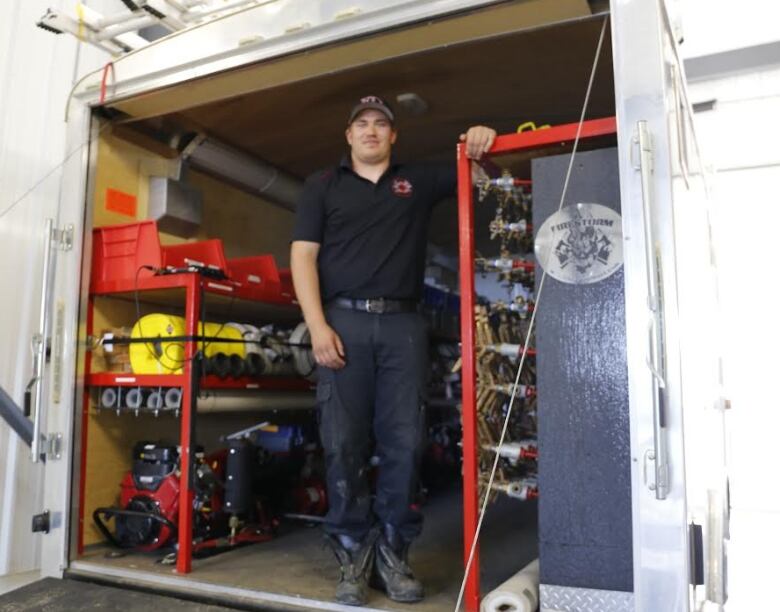
Back at a fire hall in Slave Lake, Alta.,FireSmartco-ordinatorRyan Coutts flips open the door to whatlooks like a horse trailer.
"We have two sprinkler trailers we call them," Coutts said. "They're set up with150 sprinklers and pumps and hoses and everything, so you can actually set up a sprinkler on houses."
Couttsand his teamdrove thetrailers 250 kilometresfrom Slave Lake to Fort McMurray to help save buildings during the massive wildfire this month.
That fire destroyedmore than 2,400 structuresand burnedmore than 229,000 hectares of forest.
Coutts saidoncethe sprinklers are in place, they create a dome of water over a building.The resultingbubble of moisture drives the relative humidity up.
"It gives you a better chance if embers and stuff are falling on top of your house," Coutts said.
Thetrailers were purchased after the massive wildfire of 2011 took out one-third of Coutts's hometown.
Inside the inferno
But new firefighting tools are also being developed in the lab, wherescientists are looking atwind and weather, questioningwhat they thought they knew about wildfire and its behaviour.
At the Canadian Forest Service's Northern Forestry Centre headquarters in Edmonton, fire research scientist Kerry Anderson analyses weather information from 2,500 weather stations across North America and data from satellites passing overhead.
"We enter that into the Canadian forest fire danger rating system to assess what the valuesare and what the fire danger is across the country," he said.

It's useful information that is thenpassed along to the public heading out camping or hiking aboutthe level of risk for firefrom low to extreme.
They also monitor fires that are burning and try to predict where they'll go next using computer models to spread a forest fire into the future.
A three-dimensional model capturesthe spread of fire vertically and horizontally and factors in the types of trees in a fire's path.
This desk work is being backed up with experimental test burns.Using water-cooled cameras, researchers areable to capture images of what fire looks likes and, more importantly, acts like inside an inferno.
You can see video for yourself atcbc.ca/ideas.
The images surprised even experts like University of Alberta wildfire professor Mike Flannigan.
He said the winds on the periphery of a blazeduring one test burn near Carott Lake, B.C.,were clocked at 12 km/h, while inside the fire, they were four times that.
"The fire-generated winds were much stronger than I anticipated and the way the fire spread was completely different," he said. "It was a whole bunch of little spots, almost like raining embers."
It was not at all like the surface fire Flannigan expected to see creeping forward.
Communicating what you know now
While predicting how a fire might behave is one thing, communicating that information to the people you're trying to protect is another, saidKevin Tolhurst, a fire ecology professor at the University of Melbourne inAustralia.
He points to a fire simulator he's helped develop called Phoenix.
It allows experts to factor in wind, terrain and humidity and communicate that to decision makers and the public in real time.
"You can have it all on your smartphone, your computer, your smartwatch. The information you can get now is just amazing," saidTolhurst.
The technologyis also changing what firefighters carry into Canadian forests.
Jason Cottingham, an Alberta wildfire management specialist,reaches into the large front pocket of his green cargo pants andpulls out a red book.
"It's our bible. It essentially details how we're going to fight fire," he said.
"It's a field guide of how fire behaves on the landscape based on the fuels it's burning in and the weather conditions that it's experiencing," Cottingham said.
The charts, formulas and equations in the red book give firefighters a sense of what the fire might do next.
But Cottingham admits most of the fighters rely on an app for their phone basically the bible at the click of a button.












_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)