Lack of information on China's COVID-19 surge stirs global concern
Six countries have announced testing requirements for passengers from China, including Italy and the U.S.
Moves by several countries to mandate COVID-19 tests for passengers arriving from China reflect global concern that new variants could emerge in its ongoing explosive outbreak and that the government may not inform the rest of the world quickly enough.
There have been no reports of new variants to date, but China has been accused of not being forthcoming about the virus since it first surfaced in the country in late 2019. The worry is that it may not be sharing data now on any signs of evolving strains that could spark fresh outbreaks elsewhere.
The U.S., Japan, India, South Korea, Taiwan and Italy have announced testing requirements for passengers from China, with the U.S. citingboth the surge in infections and what it said was a lack of information, including genomic sequencing of the virus strains in the country.
Authorities in Taiwan and Japan have expressed similar concern.
"Right now the pandemic situation in China is not transparent," Wang Pi-Sheng, the head of Taiwan's epidemic command centre, told The Associated Press. "We have a very limited grasp on its information, and it's not very accurate."
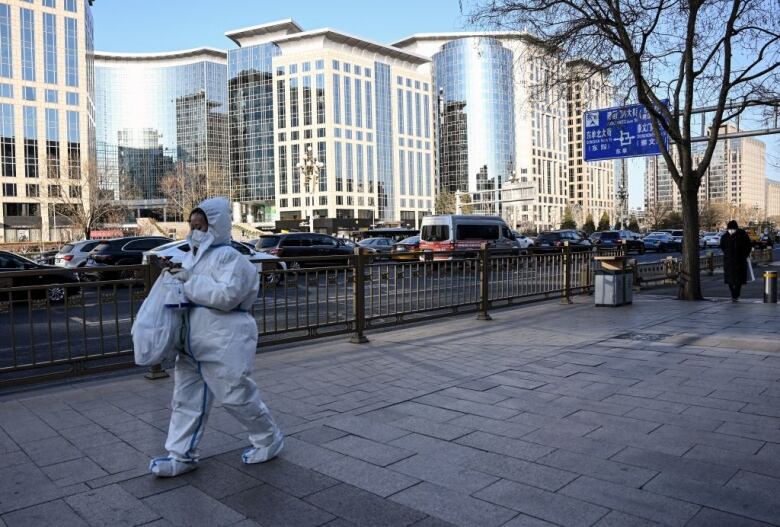

The island will start testing everyone arriving from China on Jan. 1, ahead of the expected return of about 30,000 Taiwanese for the Lunar New Year holiday later in the month.
The new Japanese rules, which restrict flights from mainland China, Hong Kong and Macao to designated airports beginning Friday, are already disrupting holiday travel plans.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Wang Wenbin noted Thursday that many countries have not changed their policies for travellers from China and said that any measures should treat people from all countries equally.
Every new infection offers a chance for the coronavirus to mutate, and it is spreading rapidly in China. Scientists can't say whether that means the surge will unleash a new mutated variant on the world,but they worry that might happen.
China: 'We keep nothing secret'
Chinese health officials have said the current outbreak is being driven by versions of the omicron variant that have also been detected elsewhere, and a surveillance system has been set up to identify any potentially worrisome new versions of the virus.
Wu Zunyou, the chief epidemiologist at China's Centre for Disease Control, said Thursday that China has always reported the virus strains it has found in a timely way.
"We keep nothing secret," he said. "All work is shared with the world."
Italy's health minister told the Senate that sequencing indicates that the variants detected in passengers arriving from China are already in circulation in Europe.
"This is the most important and reassuring news," Orazio Schillaci said.
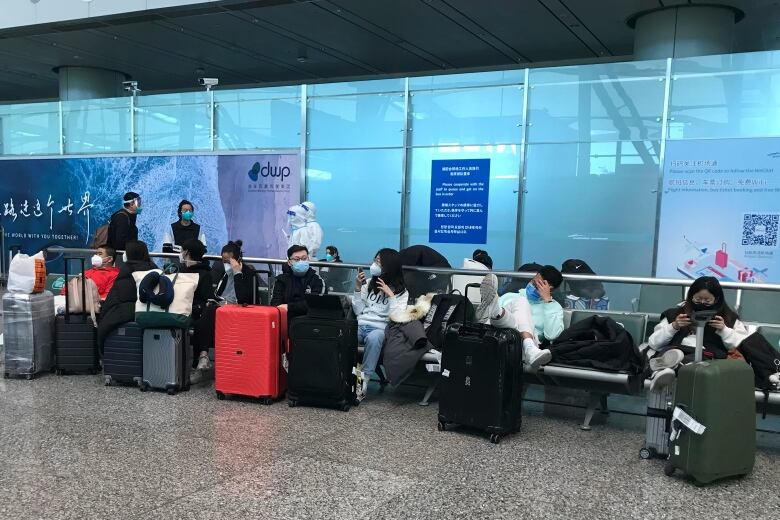

That squares with what the European Union's executive branch has said. The EU refrained Thursday from immediately following member country Italy in requiring tests for visitors from China, but said it is assessing the situation.
More broadly, World Health Organization (WHO) director general Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus has said the body needs more information on the severity of the outbreak in China, particularly on hospital and ICU admissions, "in order to make a comprehensive risk assessment of the situation on the ground."
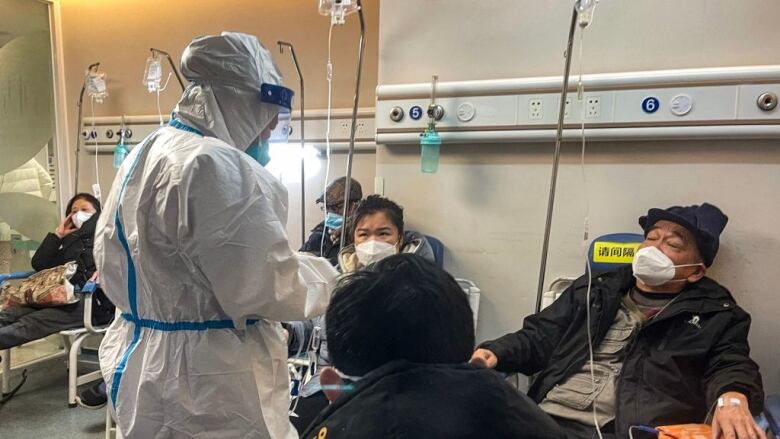
Shortages of medicine, long lines at Chinese clinics
China rolled back many of its tough pandemic restrictions earlier this month, allowing the virus to spread rapidly in a country that had seen relatively few infections since an initial devastating outbreak in the city of Wuhan.
Spiraling infections have led to shortages of cold medicine, long lines at fever clinics, and at-capacity emergency rooms turning away patients.
Cremations have risen several-fold,with a request from overburdened funeral homes in one city for families to postpone funeral services until next month.
Chinese state media has not reported the fallout from the surge widely and government officials have blamed Western media for hyping up the situation.
The global concerns, tinged with anger, are a direct result of the ruling Communist Party's sudden exit from some of the world's most stringent anti-virus policies, said Miles Yu, director of the China centre at the Hudson Institute, a conservative think tank in Washington, D.C.
"You can't conduct the lunacy of 'zero-COVID' lockdowns for such a long period of time and then suddenly unleash a multitude of the infected from a caged China to the world," risking major outbreaks elsewhere, Yu said in an email.
Dr. David Dowdy, an infectious disease expert at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, said the move by the U.S. may be more about increasing pressure on China to share more information than stopping a new variant from entering the country.
China has been accused of masking the virus situation in the country before. An AP investigation found that the government sat on the release of genetic information about the virus for more than a week after decoding it, frustrating WHO officials.
The government also tightly controlled the dissemination of Chinese research on the virus, impeding cooperation with
international scientists.
Research into the origins of the virus has also been stymied. A WHO expert group said in a report this year that "key pieces of data" were missing on the how the pandemic began and called for a more in-depth investigation.











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)