How you can help scientists spy on wildlife in hard-to-reach places
University of Guelph researcher seeks volunteers to put wildlife cameras in their backyards

More and more scientists are counting onteachers, students, hunters, urban animals-lovers and other volunteers to help them spy on and identify wildlife in their backyards and across the province or state they live in and that meansnew opportunities for anyone whowants to get involved in science.
Scientists and governments need good population data to make science-based decisions and policies to protect wildlife, from hunting quotas to outdoor cat bans.
But counting birds and animalsis also harder than it looks, especially when they're spread out over huge regions of a country or continent, including private lands and remote areas.
That's why manyscientists are relying onvolunteers called "citizen scientists" to help them collect data withtechnologylike automated cameras and recorders, and internetappsthat allow people help remotely from their home computer.
This week, scientists from across the continent gathered at the North American Congress for Conservation Biology, where somediscussed the benefits of combining citizen scienceandspace science to monitor animal populations.

Among them was Phil Townsend, a University of Wisconsin biologist who runs a project to count deer, bears and other large animals across the state using a network of thousands of motion-activated cameras distributed by volunteer citizen scientists,including teachers, their students, landowners and nature lovers.
He presented the project in a session organized by NASA about some of the projects it funds.
Townsend said information about the distributionand populationof deer and their predators is important to governments for setting hunting quotas and conservation policies.But it's also useful to other groups like hunters, farmers, ranchers, wildlife enthusiasts and the tourism industry. And by tracking that information over time, scientists will be able to see how the animals are affected by things like urban and industrial development, as well asclimate change.
Less bias, better coverage
Traditionally, he said, wildlife population data has been collected through methods like hunters' reports, roadside surveys or surveys from aircraft.
"But for every different animal species, the data might be collected a different way and might be highly biased in terms of its location and its sampling method," he said.
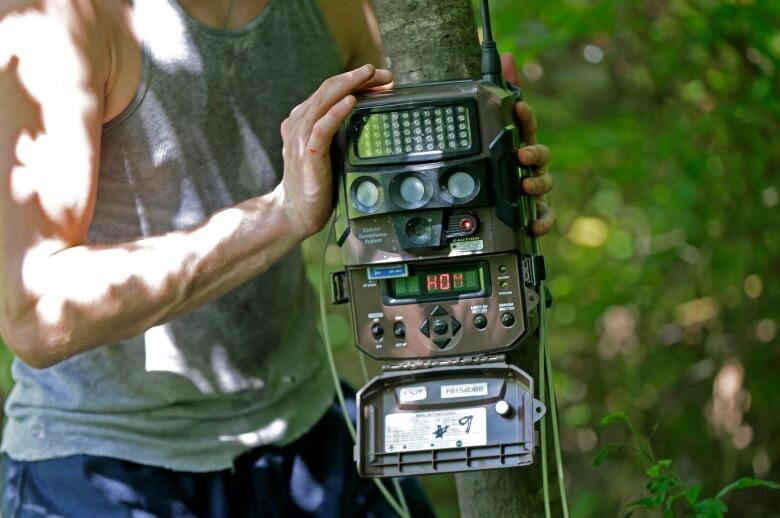

Cameras, on the other hand, record the same way everywhere, year-round, and once positioned, can record for long periods of time.
Bringing volunteers into the mix allows scientists to cover a lot more ground including places where scientists wouldn't normally have permission to survey.
"By working with citizen scientists who put out these cameras on their own private property, we're now able to characterize areas that we wouldn't otherwise be able to go into," Townsend said.
He added that volunteers feel they're getting something back too: "People love animals;people want to know what animals are on their property."
Many also want the government to have better information on which to base conservation decisions.
2 ways to help
The local volunteers set up the cameras, each worth about $100, and check them regularly to make sure the batteries are charged. They also take out the memory card periodically, check the photos, remove any that include people, and upload the remaining photos to a website called Snapshot Wisconsin.
Then volunteers from all over the world take over, going through the photos to identify the animals in them.
"And it's almost like a game," Townsend said. "It's so much fun. It's really addictive, actually."

The data is thenoverlaid with satellite data to show what types of vegetation are linked with different wildlife populations.
"The satellite fills in the gaps We can predict [animal distributions] for places between where all the trailcams are."
Matthew Clark, a professor at Sonoma State University in California, presented a similar NASA-funded project to monitor what kinds of birds live in different parts of nearby Sonoma County.
The project, called Soundscapes to Landscapes, used volunteers to distribute sound recorders around the county that automatically take one-minute recordings every 10 minutes of surrounding bird tweets, chirps, twitters and songs. The researchers used machine learning to train computers to automatically identify the birds in the recordings.
Like Townsend, he plans to combine the citizen science data with satellite data to see what types of vegetation are important to which bird species.
Clark, Townsend and other biologists will be getting an extra eye in the sky in the fallwhen a new type of remote sensor gets installed on the International Space Station. The Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) will send laser pulses down to Earth and measure the light that's reflected back to map different layers of vegetation from the ground to the top of the forest canopies around the world.
In Canada, some similar citizen science projects are also underway.
Counting cats
Earlier this year, the City of Calgary launched Calgary Captured, which asks volunteers from the public to identify animals in photos taken by motion-activated cameras in 12 city parks.
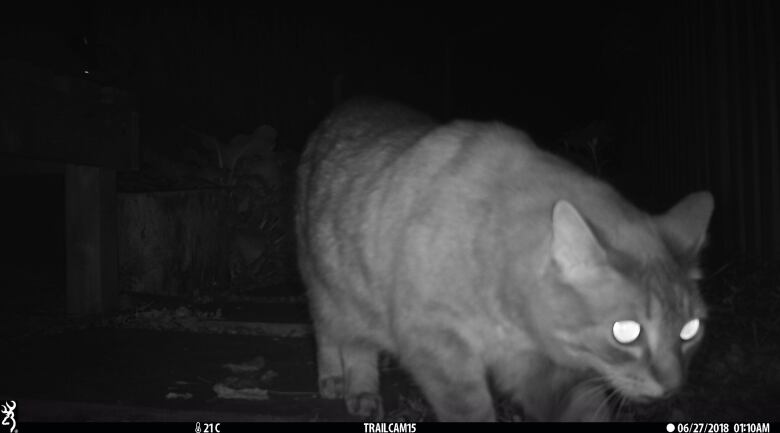

And University of Guelph biologist Elizabeth Gow is currently recruiting volunteers willing to buy and install infrared cameras in their backyards and on their rural properties to record images of nighttime prowlers, including raccoons, skunks and especially cats.
Gow, a postdoctoral researcher who holds a Liber Ero fellowship, hopes to get a good estimate of how many outdoor, stray and feral cats there are in Wellington County around Guelph and elsewhere southern Ontario, and to determine where cat populations are the most dense.
Where there are too many cats, they can spread diseases such as rabies,Lyme disease andtoxoplasmosis to both other cats and humans, said Gow. Theycan also be devastating to wildlife such as songbirds. In Canada alone, conservationists estimate cats kill 200 million birds a year.
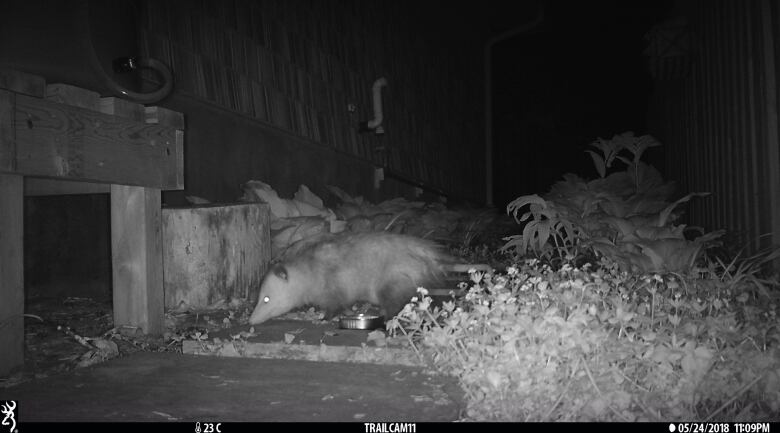

Gow hopes that getting better data will help cities take the right steps to manage cats and protect wildlife, such as bylaws banning outdoor cats or running programs to trapferal cats in some places.
But she said volunteers who help out get something back, too a chance to spy on what's happening in their own backyards at night.
"I think it's really exciting. It's an opportunity, if you're interested in animals, to kind of get this behind-the-scenes look of what's going on."











_(720p).jpg)


 OFFICIAL HD MUSIC VIDEO.jpg)
.jpg)